Water soluble vitamins such as Vitamin C and B Vitamins are excreted in urine when it’s not absorbed. Water soluble vitamins rarely accumulate to toxic levels. Fat soluble such as Vitamin A, D, E, and K are different. The body stores excess vitamins fatty tissue and the liver for future use. The body does an excellent job absorbing and storing fat soluble vitamins so it is important to be mindful of the intake of fat-soluble vitamins.
There are different forms of each fat-soluble vitamin, if you are concerned about quality and benefits, is important to understand the forms especially with Vitamin E.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A stimulates the production and activity of white blood cells, takes part in remodeling bone, helps maintain healthy endothelial cells (those lining the body’s interior surfaces), and regulates cell growth and division such as needed for reproduction. Vitamin A is found in orange and yellow vegetables like carrots, bell peppers, and sweet potatoes. Leafy green vegetables are also rich in vitamin A.
In supplements, two different forms of Vitamin A are used:
There are two types of supplemental vitamin A
- pre-formed vitamin A (retinol, retinyl palmitate, retinyl acetate)
- provitamin A (beta-carotene)
Preformed vitamin A (retinyl palmitate, retinyl acetate) is effectively absorbed, stored, and hydrolyzed (broken down by water molecules) to form retinol, provitamin A.
Provitamin A (β-carotene) is less easily digested and absorbed, and must be converted to retinol and other retinoids by the body after uptake into the small intestine.
Supplements use pre-formed vitamin A (retinyl palmitate, retinyl acetate) and provitamin A (β-carotene) or a combination of both.
Because preformed vitamin A is effectively absorbed and stored, there is a risk of toxicity when taken in high amounts. In contrast to preformed vitamin A such as retinyl palmitate or retinol, beta-carotene is not toxic even at high levels of intake. The body can form vitamin A (retinol) from beta-carotene as needed, and there is no need to monitor intake levels as with preformed vitamin.
Companies take these factors in to considerations when choosing the amount of pre-formed vitamin A and provitamin A and the ratio of pre-formed vitamin a to provitamin A. It is beneficial and safer to combine provitamin A (beta-carotene) with previtamin A (retinyl palmitate) for daily supplementation.
Preformed Vitamin A (retinyl palmitate) is immediately absorbed and stored as retinol. The body forms more vitamin A (retinol) from provitamin A (beta-carotene) as needed.
If the supplement utilizes beta-carotene for Vitamin A, you may need higher amounts of Vitamin A for benefits, because the body must convert it first.
If the supplement utilizes retinyl palmitate for Vitamin A, you may have to be mindful and use caution to make sure you don’t take high doses of preformed Vitamin A.
Choose a company with expertise that formulates their multi-vitamin with these factors in mind.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is known as the “sunshine vitamin”. Vitamin D is responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate and other biological processes.
It’s been promoted in recent years especially for its benefits for:
- Immune support
- Uplifting mood
- Cardiovascular and metabolic support
The primary source of vitamin D is sunlight.
The following is the process of how your body converts UVB light to cholecalciferol which converts 25-hydroxycholecalciferol and to 1,25-dihidrocycholecalciferol.
- When you skin is exposed to sunlight, the sun’s Ultraviolet B (UVB) interacts with a protein called 7-DHC in the skin converting it to Vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol.
- Within the liver, cholecalciferal is hydroxylated to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol by the enzyme 25-hydroxylase. (Vitamin D tests check for 25-hydroxycholecalciferol)
- Within the kidney, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol serves as a substrate for 1-alpha-hydroxylase, yielding 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, the biologically active form.
There several reasons why people are deficient in Vitamin D.
The primary reason is decreased exposure to sunlight.
- This can be due to lifestyle in staying indoors or living in a parts of the world that has limited sunlight, especially between October and March in the northern hemisphere.
- People with darker skin pigment have higher levels of melanin. Melanin absorbs ultraviolet B (UVB) rays and reduced vitamin D production.
- Sunscreen can also reduce vitamin D production
Other reasons why people are deficient in Vitamin D cholecalciferol are liver and kidney issues because they are responsible for converting Vitamin D to its active form.
Vitamin D is found is a small number of foods: oily fish, red meat, liver, and egg yolks. Because of this Vitamin D is added to foods such as milk and breakfast cereals.
However, if people aren’t exposed to sunlight (or converting enough sunlight) and aren’t consume enough Vitamin D in their foods, then they have low levels of Vitamin D. This may lead to low energy, poor immune function, and other health issues.
Vitamin D deficiency is a growing issue in modern society. Vitamin D supplementation is a must for many people that aren’t receiving Vitamin D through other means.
Vitamin D supplements are available in two forms:
- Vitamin D2 – ergocalciferol (plant based)
- Vitamin D3 – cholecalciferol (animal based) (also the same type of Vitamin D our bodies produce when our skin is exposed to the sun)
Vitamin D, in its D3 form, is more potent and better absorbed form than its D2 form. Studies have found that vitamin D3 effectively raises blood vitamin D levels for a longer period than vitamin D2.
How most Vitamin D3 is made
Vitamin D3 is derived from lanolin from sheep’s wool.
- 7-dehydrocholesterol extracted from the lanolin found in sheep’s wool
- 7-dehydrocholesterol is exposed to UV light to form preform vitamin D3 and then heated to form vitamin D3.
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is standard and is the form of Vitamin D that is used by most companies.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E supports cardiovascular health, immune system, promote eye health and prevents inflammation. The main function of α-tocopherol in humans is that of a fat-soluble antioxidant. Fats, which are an integral part of all cell membranes, are vulnerable to damage through lipid peroxidation by free radicals. α-Tocopherol is uniquely suited to intercept peroxyl radicals and thus prevent a chain reaction of lipid oxidation. It is commonly found is plant based oils and in foods such as nuts and seeds.
There are eight forms of vitamin E
- Alpha-tocopherol
- Beta-tocopherol
- Gamma-tocopherol
- Delta-tocopherol
- Alpha-tocotrienol
- Beta-tocotrienol
- Gamma-tocotrienol
- Delta-tocotrienol
Alpha-tocopherol is the body’s preferred form of vitamin E.
Why is natural alpha-tocopherol better than synthetic alpha-tocopherol?
There are different isomers (structures) of alpha-tocopherol.
In the supplement industry, natural alpha-tocopherol is commonly labeled “d alpha tocopherol.”
Synthetic alpha-tocepherol is commonly labeled ” dl alpha-tocopherol.”
This nomenclature (name choice) is technically incorrect because it implies just two isomers (structures) of alpha-tocopherol. There are actually eight stereoisomers of alpha-tocopherol. Although the name choice is misleading, the name choice makes it easier to identify and is now standard.
Synthetic alpha tocopherol or “dl alpha tocepherol” is a mixture of eight stereoisomers of alpha-tocopherol
- RRR-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
- RSR-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
- RRS-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
- RSS-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
- SRR-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
- SSR-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
SRS-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position - SSS-configuration at the 2, 4’, and 8’-position
While the formula and molecular weight of synthetic alpha-tocopherol is the same as natural alpha-tocepherol, only the R-conformation at position 2 of alpha-tocopherol meet the Vitamin E requirements.
In other words, natural alpha-tocopherol with only one configuration is superior to synthetic alpha-tocopherol, a mixture of eight configurations.
RRR configuration alpha tocopherol (natural alpha tocopherol) is the most bioavailable form of Vitamin E. alpha-tocopherol is the form of vitamin E that is preferentially absorbed and accumulated in humans. While we obtain Vitamin E in our foods, gamma-tocopherol is the most common in American diet due to prevalence of soybean and corn oil.
Why is it beneficial to have all forms of natural Vitamin E than just natural alpha-tocopherol?
Natural alpha-tocopherol is the most bioavailable and preferentially retained by the liver. The other natural forms of Vitamin E are known to be potent antioxidants and provide additional benefits. Tocotrienols and gamma-tocopherol are thought to be better scavengers of peroxyl radicals and reactive nitrogen species than alpha-tocopherol. Tocotrienol may provide benefits that tocopherols may not provide.
What is the source of Vitamin E?
Natural Vitamin E n supplements come from a variety of sources. The most common is soybean oil, safflower sunflower oil. The label may not indicate where the Vitamin E is sourced, so you may have to contact the company direct to find out where it is source. The best source of Vitamin E is soy-free, so look for a soy-free source like safflower oil or sunflower oil.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays an important role in wound repair. It also supports cardiovascular health and cardiovascular health. The primary food source of Vitamin K is leafy greens. Because Vitamin K increases a person’s ability to repair wounds and clot, the amount in supplements should be evaluated for people that are on blood thinning medication.
There are two types of Vitamin K:
- Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone and phytonadione)
- Vitamin K2 (menaquinone-4 “MK-4” and menaquinone-7 “MK-7”)
Vitamin K1 and Vitamin K2 (MK-7) are absorbed and accepted by the body. Vitamin K2 (MK-7) may provide additional benefits because it has a longer half life meaning it stays in the body longer.
Vitamin K1 is the most common form of vitamin K found in the diet. Because most people get adequate amounts of Vitamin K in their diet, it is not necessary to include a large amount of vitamin K in a supplement.
dōTERRA’s multivitamin Microplex VMz utilizes beneficial forms of fat soluble vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E, and K)
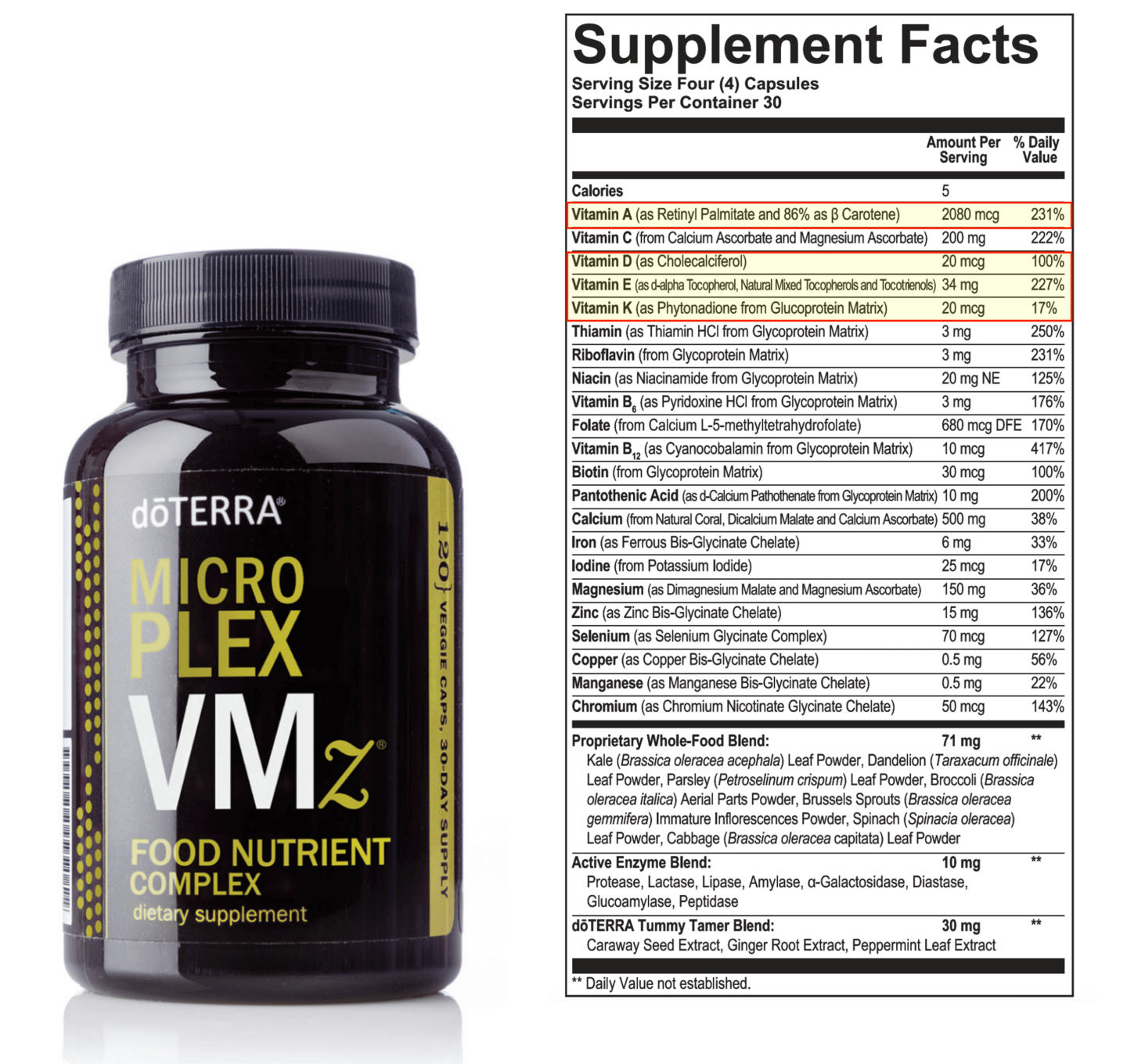
Vitamin A.
Microplex VMz utilizes a combination of beta-carotene and retinyl palmitate in a ratio that is beneficial for daily supplementation.
The composition of Vitamin A in Microplex VMz:
- ~86% beta-carotene (provitamin A)
- ~14% retinyl palmate (preformed Vitamin A)
Vitamin D
Microplex VMz utilizes Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) which is standard in supplementation
Vitamin E
Microplex VMz utilizes a natural mixture of all forms of Vitamin E (natural mixed tocopherols and natural mixed tocotrienols) which is the most complete and best form of Vitamin E. Microplex VMz utilizes sunflower oil, a soy-free source of Vitamin E.
- natural alpha-tocopherol
- natural beta-tocopherol
- natural gamma-tocopherol
- natural delta-tocopherol
- natural alpha-tocotrienol
- natural beta-tocotrienol
- natural gamma-tocotrienol
- natural delta-tocotrienol
Vitamin K
Microplex VMz utilzes a fermented form of Vitamin K to create a glycoprotein matrix bound Vitamin K. Feremented vitamins are treated as food. They are bioavailable and gentle on the GI tract. I wrote an article explaining the benefits of fermented vitamins here.
doTERRA’s multivitamin Microplex VMz provides 22 essential vitamin and minerals. Microplex VMz utilizes the most beneficial form of each vitamin and minerals.
I’ve written what ingredients or forms of nutrients to look for in a multivitamin or supplement in the following articles:
Multivitamin
Water Soluble Vitamins (B Vitamins + Vitamin C)
Fat Soluble Vitamins (Vitamin A, D, E, and K)
Macrominerals (Calcium and Magnesium)




